What is a coordinate plane?
The coordinate plane is a grid formed by two number lines that cross each other at a point called the origin. It helps us locate and describe positions using pairs of numbers called coordinates.
- The horizontal line is called the x-axis.
- The vertical line is called the y-axis.
- They meet at the origin (0, 0).
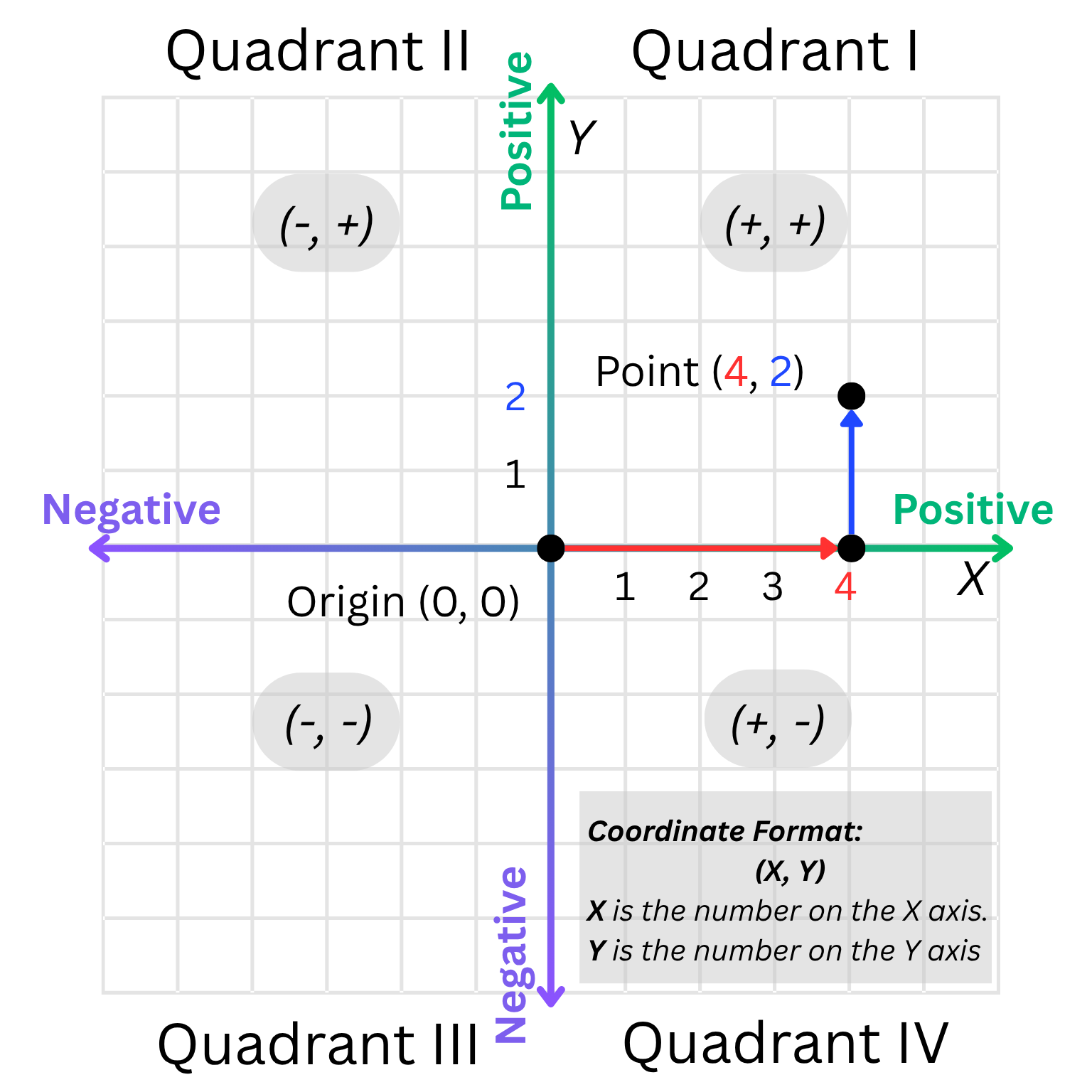
The coordinate plane helps us describe where objects are located or to show data using points.
Understanding coordinates and points
A coordinate tells where a point is located on the plane. Each point is named using an ordered pair of numbers written in parentheses, like (x, y).
- The point (4, 2) means:
- Start at the origin (0, 0).
- Move 4 units to the right along the x-axis.
- Move 2 units up along the y-axis.
Always read or write coordinates in the order (x, y). The first number tells you how far to move right or left, and the second tells you how far up or down to move.
The four quadrants
The coordinate plane is divided into four parts called quadrants. Each quadrant shows a different combination of positive and negative numbers.
- Quadrant I: (+, +)
- Quadrant II: (−, +)
- Quadrant III: (−, −)
- Quadrant IV: (+, −)
In fifth grade, you usually work only in Quadrant I, where both numbers are positive.
Plotting points on the coordinate plane
Plotting a point means marking the location of an ordered pair on the coordinate plane. You start from the origin and move along the x-axis and y-axis based on the numbers in the pair.
- Start at (0, 0), the origin.
- Move right (for positive x) or left (for negative x).
- Move up (for positive y) or down (for negative y).
- Place a point at that spot and label it with its coordinates.
Check your work by making sure your point lines up with both the x and y values correctly.
Using coordinates to solve problems
The coordinate plane can be used to represent patterns, compare data, or find distances between points.
- Point A is at (2, 3) and Point B is at (2, 6).
- Both points are on the same vertical line, so the distance between them is 3 units up and down.
Look for patterns in coordinates to help you understand shapes, graphs, or movements on the plane.